
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
Everything you need to know about Rolls Royce
Rolls-Royce Holdings plc Company Profile
Rolls-Royce (LON: RR) is a British multinational aerospace and defence company incorporated in February 2011. The company owns Rolls-Royce, a business established in 1904 that today designs, manufactures and distributes power systems for aviation and other industries.
Their range of products goes from advanced technologies for defence businesses as well as land, naval, aerospace, submarines, and services. It is the world's second-largest aircraft engine maker and has major marine propulsion and energy businesses. (Source: artsandculture.google.com)
In 2018, Rolls Royce became the 16th defence contractor in terms with when measured by defence revenues. (Source: Rolls-Royce 2018 annual report). The company is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a part of the FTSE 100 Index.
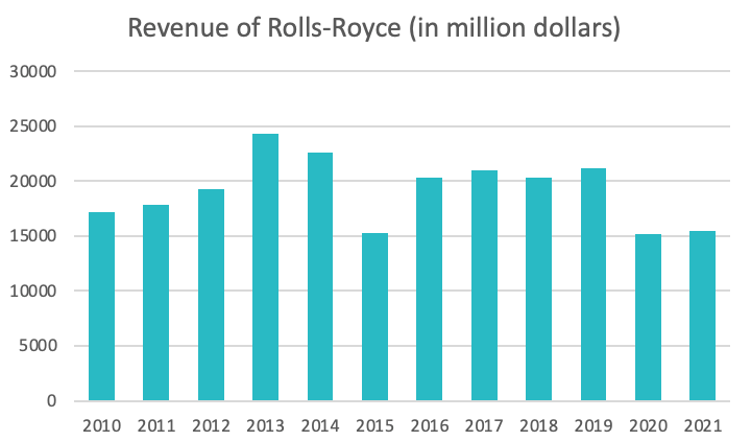
Source : macrotrends.com
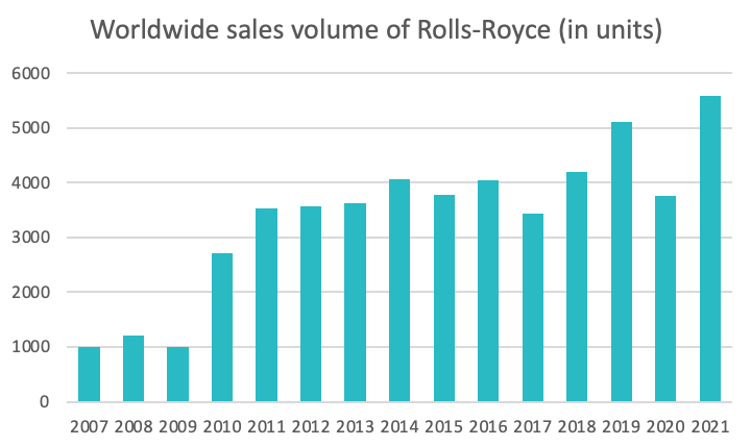
Source : statista.com
Rolls-Royce History
In 1904 Rolls Royce was established as a luxury car manufacturer and then later expanded to an aero-engine manufacturing business in Manchester, the United Kingdom by the partnership of Charles Rolls and Henry Royce.
The First World War brought them into manufacturing aero-engines. Joint development of jet engines began in 1940 and they entered production. Rolls-Royce has built an enduring reputation for developing and manufacturing engines for defence and civil aircraft.
In 1971, the owners were obliged to liquidate their business. The useful portions were bought by a new government-owned company created for the purpose named Rolls-Royce (1971) Limited which continued the core business. In 1973 Rolls Royce Motor cars Limited were separated from the main company. Rolls-Royce plc finally returned to the stock market in 1987.
On 14 June 2018, the company announced restructuring the business to create three simpler decentralised units (civil aerospace, defence and power systems).
Rolls-Royce (LON: RR) is a defence and aerospace company. This is a sector in which international demand is unevenly distributed between countries. The ability to defend oneself is a natural desire expressed since the beginning of civilizations. It is of course a sector very prone to innovations, which companies must imperatively take into account to remain competitive. As a result, we observe a demand that is renewed with each innovation.
It is also a sector very much impacted by the global and national geopolitical context. Indeed, the customers of this sector are not individuals but state, governed by various laws and budgets, which makes it a much more complex market to predict. The current context between Russia and Ukraine, which strongly benefits this market, is one proof.
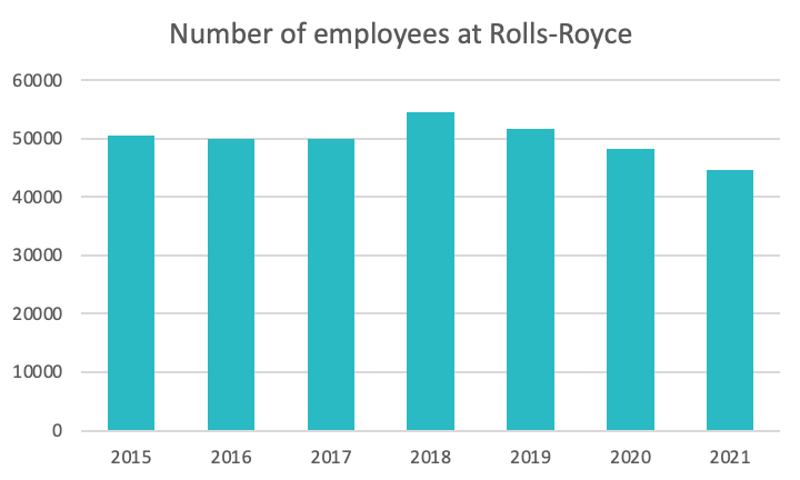
Source : macrotrends.com
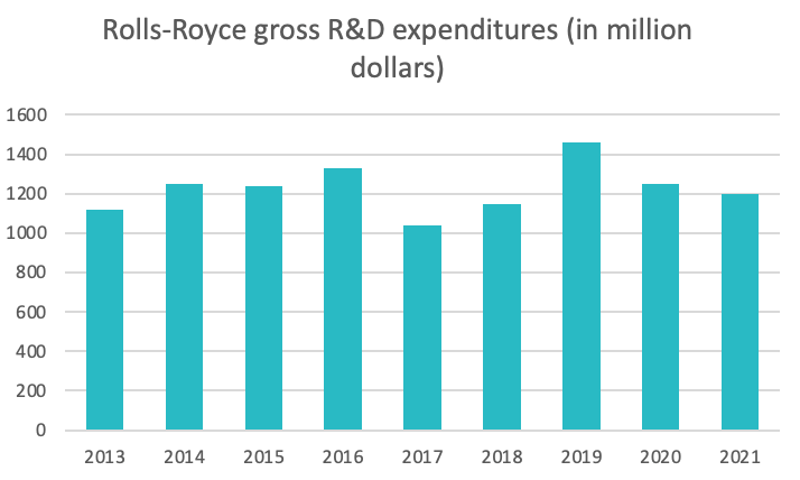
Source : statista.com
Rolls Royce Acquisitions
- In 1988 Rolls Royce acquired Northern Engineering Industries (NEI), a group of heavy engineering companies primarily associated with power management and electrical generation based in North East of England. The group of companies includes Clarke Chapman (Cranes), Parsons, and Ryerolle. Later these companies were renamed Rolls Royce Industrial Power Group. (Source: Nytimes)
- Further, on November 21, 1994, Rolls Royce announced their intention to acquire the Allison Engine Company. Allison Engine is a manufacturer of gas turbines and components in America catering to aviation, marine engines and industrial sectors. Since the company had its involvement in classified export restricted technology this acquisition was still subject to investigation to regulate the national security implications. The US Department of Defence on March 27, 1995, announced that this deal will not endanger national security. However, Rolls-Royce was obligated to set up a proxy board to manage Allison and to create a separate entity Allison Advanced Development Company, Inc.
- The deal was done for $525 million and it bought four new engine types into the Roll-Royce civil engine portfolio on around seven platforms and various light aircraft applications. Allison Engine is now known as Rolls-Royce Corporation, a part of Rolls0Royce North America. (Source: Los Angeles Times)
- In 1999 Rolls Royce acquired Vickers Plc. The company was acquired for its marine business and later around the year 2002 the company was sold to Alvis Plc. (Source: BBC News)
- The company gained a leading position in the corporate and regional airline sector through the development of the Tay engine. This engine was developed by Allison's acquisition and the consolidation of BMW and Rolls-Royce joint venture. Later, in 1999 BMW Rolls Royce was renamed Rolls-Royce Deutschland and became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Rolls-Royce Plc. (Source: UK Defence Forum)
- In 1999 Rolls-Royce and Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC) formed a joint venture and created Optimized Systems and Solutions Limited (formerly known as Data Systems & Solutions). Later in 2006, SAIC exited the joint venture and made Rolls-Royce the sole owner. (Source: DBPedia)
- In March 2011, Daimler AG and Rolls-Royce established a $4.2 billion public tender offer to acquire 100% shares of Tognum AG. It is the owner of MTU Friedrichshafen a high-speed industrial and marine diesel engine manufacturer. Tognum was acquired by a 50:50 joint venture. Both Rolls-Royce and Daimler intend to list Tognum on Frankfurt Stock Exchange. Tognum also incorporates the existing Rolls-Royce business called Bergen Engine business. (Source: Rolls-Royce Press Release)
- Following the acquisition of Goodrich by United Technologies Corporations, it was announced by Rolls-Royce in July 2012 that they would purchase Goodrich’s 50% stake in Aero Engine Controls. The company became a wholly owned subsidiary of Rolls-Royce after this transaction. (Source: Rolls-Royce Press Release)
- At Paris Air Show in June 2019 the company announced the acquisition of Siemens’ electric propulsion branch. (Source: aerospace manufacturing)
Key Figures and Financial Ratios
Market capitalization: £5.766 billion1[October 3, 2022]
Revenue: £10.947 billion2[2021]
Net income: £124 billion 3[2021]
Dividends paid: Twice a year 4
Earnings per share: £1.48 5[2021]
Forward Price to earnings ratio: ≃18.22x 6[2022]
Debt to equity ratio: 11.67x77[2022]
Source : macrotrends.com
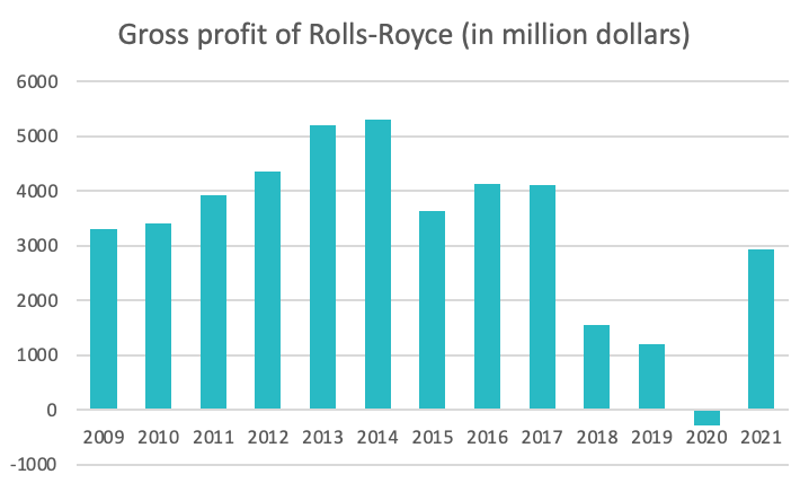
Source : macrotrends.com
Graniteshares Offering Products
Rolls Royce
Sources
- Finance Yahoo
- Annual Report Rolls-Royce
- Annual Report Royce
- Rolls-Royce Holdings Plc dividendmax
- Annual Report Rolls-Royce
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc (RR.L)Yahoo Finance
- Rolls-Royce Holdings Debt-to-Equity gurufocus
DISCLAIMER
Please note that GraniteShares short and leveraged Exchange Traded Products are for sophisticated investors.
This is a disclaimer stating that all trading and investing comes with risks. Always do your research and do not invest more than you can afford to spend.
GraniteShares accepts no responsibility for any loss or damage resulting directly or indirectly from the use of this blog or the contents.
This blog does not constitute an offer to buy or sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy securities in any company. Nothing contained herein constitutes investment, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied upon in making an investment or other decision. No recommendation is made positive or otherwise, regarding individual securities or investments mentioned herein. Any summary list of risk factors does not purport to be a complete enumeration or explanation of the risks involved in a particular investment. Prospective clients must consult with their own legal, tax and financial advisers before deciding to invest. This email contains the opinions of the author, and such opinions are subject to change without notice. The source of data is GraniteShares unless otherwise stated. No guarantee is made to the accuracy of the information provided which has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable. This email and the information contained herein is intended only for the use of persons (or entities they represent) to whom it has been provided. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. The value of an investment may go down as well as up and can result in losses, up to and including a total loss of the amount initially invested. Investments may involve numerous risks including, among others, company risks, general market risks, credit risks, foreign exchange risks, interest rate risks, geopolitical risks, and liquidity risks.



